1.
Is not a part of the sustainable development?
A.
The development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the
ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
B.
The ability of a society, ecosystem, or any such existing system to operate continuously
in an undefined future without reaching key resource depletion.
C.
The capacity and opportunity to maintain and improve the quality of life
indefinitely without degrading quantity, quality or availability of natural,
economical and social resources
D.
To protect an individual life and societal standards.
Answer: (D)
2. Which of the
following best describes Sustainable Development?
A. Development that
provides for economic and social viability even if that results in
environmental degradation for the future
B. Development that
provides environmental sustainability even if that results in economic and
social degradation for future generations
C. Development that
meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future
generations to meet their own needs
D. Development that
meets the needs of the future generations even if that means present society's
needs go unmet
Answer:
(C)
3.
The term sustainability refers to ________.
A.
maintaining resource use at current or higher levels
B.
keeping the natural environment and human society in a happy, healthy and
functional state
C.
holding or increasing the current quality of human life
D.
always focusing on fulfilling short-term needs
E.
opposing change from current policies
Answer:
(B)
4.
Harnessing wind energy to provide power for homes, offices, and other buildings
or to pump water is one of the best examples of
--------- development.
A.
Technological
B.
Scientific
C.
Sustainable
D.
Economical
Answer:
(D)
5.
“Environmental sustainability doesn't mean living without luxuries
but rather being aware of your resource consumption and reducing
unnecessary waste”.
A.
Yes
B.
No
C.
May be
Answer:
(A)
6. Which of the
following terms describes the point beyond which the environment exceeds its
ability to provide essential resources?
A. Sustainable
Development
B. Sustainable
Consumption
C. Environmental
Development
D. Environmental Limits
Answer: (D)
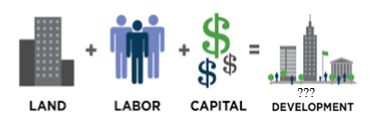
7. Which type of development is
represented by figure given below
A. Social development
B. Economic development
C. Industrial development
D. Sustainable development
Answer: B
8. The
technology which meets the sustainable development needs is often referred to
as
A. Advanced technology
B. Appropriate technology
C. Sustainable technology
D. Adaptive technology
Answer: (B)
9. The purpose of development is ........................without
damaging the resources of the environment.
A. a rise in the level and
quality of life of the population
B. the creation or expansion of
local regional income
C. the creation or expansion
employment opportunities
D. all of the above
Answer:
(D)
10. The four domains of
sustainability are...................
A. economic,
ecological, political and cultural
B. economic, social,
political and cultural
C. economic,
ecological, social and cultural
D. economic,
ecological, political and social
Answer:
(A)
11. The
integration of the three pillars of sustainable development do not include
A.
Bearable + Equitable = Social Equity
B.
Bearable + Viable = Environmental protection
C.
Equitable + Viable = Economical viability
D.
Human + Viable = Human Sustainability
Answer:
(D)
12. Which
of the following is/are not an objective (s) of sustainable development?
A.
To bring about a gradual and sometime catastrophic transformation of
environment
B.
Prevention of global warning
C.
Reduction in toxic discharge
D.
Protection of natural environment and living creatures
Answer: (D)
13. Which
of the following is/are not an objective (s) of sustainable development?
A.
To bring about a gradual and sometime catastrophic transformation of
environment
B.
Maintain a dynamic balance of arable land and implement an agricultural
development strategy
C.
Maintain a dynamic balance of water resources by reducing water consumption for
every unit of gross development product growth and agricultural value added
D.
Protection of natural environment and living creatures
Answer: (D)
14. Which
of the following is/are not an objective (s) of sustainable development?
A.
To bring about a gradual and sometime catastrophic transformation of
environment
B.
Reduction of resource and energy consumption
C.
Food production and utilization
D.
Protection of natural environment and living creatures
Answer: (D)
15.
Which is not a purpose of the SDG?
A.
To promote peace
B.
To promote prosperity
C.
To promote equality
D.
To promote challenge
Answer: (D)
16.
Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future
generation to meet their own needs is given by:
A.
Brundtland
B.
Mahatma Gandhi
C.
Maathai
D.
Sunderlal Bahugana
Answer:
(A)
17.
Which two of the following are widely regarded as being important aspects of
sustainable social and economic development?
A.
Inter-generational equity
B.
Intra-generational equity
C.
Inter-generational inequity
D.
Intra-generational inequity
E.
High levels of consumption expenditure and low levels of savings
Answer:
A & B
18.
Who should be involved for the SDG to be met?
A.
Individuals
B.
Governments
C.
voluntary organizations
D.
private companies
E.
All of the above
Answer:
(E)
19.
Which SDG aims to Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine
resources for sustainable development?
A,
No Poverty
B.
Affordable and Clean Energy
C.
Life below Water
D.
Life on Land
Answer: (C)
20.
What qualities do people need to be change-makers for sustainability?
A.
Knowledge about SD
B.
Skills to encourage SD
C.
Values and attitudes that support SD
D.
Sustainable habits
Answer:
(C)
21.
The dimensions of sustainability includes
A.
Stability (Peace and Security)
B.
Cultural dimensions
C.
Institutional / administrative arrangements
D.
All of the above
Answer: (D)
22.
Is not accounted as a dimension of sustainability
A.
Environment
B.
Society
C.
Economy
D.
Industries
Answer:
(D)
23.
The unfavorable alteration of environment due to human activity is termed as
A.
Ecological disturbance
B.
Catastrophe
C.
Ecological degradation
D.
Pollution
Answer:
(D)
24.
........................ is the deterioration of the environment through
depletion of resources such as air, water and soil; the destruction of
ecosystems; habitat destruction; the extinction of wildlife; and pollution.
A.
Environmental degradation
B.
Ecological disturbance
C.
Ecological degradation
D.
Pollution
Answer: (A)
25.
...................... is defined as any change or disturbance to the
environment perceived to be deleterious or undesirable
A.
Environmental degradation
B.
Ecological disturbance
C.
Ecological degradation
D.
Pollution
Answer: (D)
26.
Which among the following can be considered as the cause(s) of poverty?
1.
Social, economic and political inequality
2.
Social inclusion
3.
Unemployment
4.
Indebtedness
5.
Unequal distribution of wealth
Select
the correct option from the below codes:
A.
1, 2, 3, and 4
B.
2, 3, 4 and 5
C.
1, 3, 4 and 5
D.
1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Answer. (D)
27. When poverty is
taken in relative term and is related to the distribution of income consumption
expenditure it’s called:
A. Law line poverty
B. Absolute poverty
C. Relative poverty
D. None
Answer: (D)
28. Vulnerability to poverty is determined
by the options for finding an alternative living in terms of
A. Assets
B. Education
C. health
D. all the above
Answer: (D)
29. The strategy
formulation for promoting a sustainable development includes
A. Country
ownership and participation,
B. Broad
consultation, including particularly with the poor and with civil society, to
open up debate on new ideas and information, expose issues to be addressed, and
build consensus and political support on action.
C. All of the above
D. None of the
above
Answer: (C)
30. The strategy formulation for promoting a sustainable
development includes
A. Country
ownership and participation,
B. Ensuring
sustained beneficial impacts on disadvantaged and marginalised groups and on
future generations.
C. All of the above
D. None of the
above
Answer: (C)
31.
The strategy formulation for promoting a sustainable development includes
A.
Country ownership and participation,
B.
A solid analytical basis, taking account also of relevant regional issues,
including a comprehensive review of the present situation and forecasts of
trends and risks.
C.
All of the above
D.
None of the above
Answer: (C)
32.
Resistance to the concept of sustainability are (select any two)
A.
Motivation
B.
Identification of the problem
C.
Cultivation pattern
D.
Forest
Answer:
A & B
33.
Resistance to the concept of sustainability are (select any two)
A.
Literacy and basic education
B.
Lack of financial resources
C.
Cultivation pattern
D.
Forest
Answer:
A & B
34.
Resistance to the concept of sustainability are (select any two)
A.
War-torn countries or political influences
B.
Natural hazards
C.
Cultivation pattern
D.
Forest
Answer: A & B
35.
Is not an alternative approach for sustainable development?
A.
Precaution
B.
Proportionality
C.
Maintenance
D.
Life-cycle approach
Answer: (D)
36.
Is not an alternative approach for sustainable development?
A.
Prevention
B.
Rehabilitation
C.
Security rule of law
D.
Environmental protection
Answer:
(B)
37.
Is not an alternative approach for sustainable development?
A.
Improved markets
B.
Agricultural development
C.
Community development
D.
Protection
Answer:
(D)
38.
Is an example of sustainable development?
A.
Ola Cab
B.
Uber
C.
Big basket
D.
Solar cooker
Answer:
(D)
39.
Is not an example of sustainable development?
A.
Wind Energy
B.
Solar Energy
C.
Big basket
D.
Green spaces
Answer:
(D)
40.
Is not an example of sustainable development?
A.
Wind Energy
B.
Solar Energy
C.
Big basket
D.
Green spaces
Answer:
(D)
41.
Merle C Crawford (1980) described four
innovation strategies:
1.
Inventive
2.
Adaptive
3.
Economic
4.
Innovative Applications
Which
one is incorrect
A.
Inventive – First to market
B.
Adaptive - Second but “best”
C.
Economic– User friendly
D.
Innovative Applications –creative use of existing technology
Answer:
(C)
42.
------------ refers to innovation that happens on an incremental basis, often
in response to customer and market demands or improvements in technology.
A.
Routine innovation
B.
Disruptive innovation
C.
Marketing innovation
D.
Radical innovation
Answer:
(A)
43. is an example
of;
A. Sustaining
innovationB. Disruptive
innovation
C. Application
innovation
D. Business
innovation
Answer: (B)
44. Focuses to address which of the two SDGs
listed below
A. Education
B. Employment
C. Poverty
D. No hunger
Answer: B & C
45.
What does Application Innovation concern about?
A.
Takes existing technologies into markets to serve new purpose
B.
Makes processes for established offerings in established markets more effective
or efficient
C.
Improves customers – touching processes, such as marketing communications or
customer transactions
D.
Capitalize on disruption to restructure industry relationships
Answer:
(A)
46.
Reorganize the jumble steps of innovation process
1.
Narrow the search Space,
2.
Look for what is missing,
3.
Why,
4.
Look for possible combination,
5.
Manage the action cycle to take it from idea to innovation
A.
1-2-3-4-5
B.
2-1-3-4-5
C.
3-2-1-4-5
D.
5-4-3-2-1
Answer:
(C)
47.
break through innovation involves
1.
implementation of new technology,
2.
customer don’t realize they need it until they experience it first hand, and
3.
for every change life as we know it.
The
best example is
A.
Electricity
B.
Computers
C.
Mobiles
D.
Automobiles
Answer:
(A)
48. A variety of principles are used in
environmental management
A. Polluter Pay
Principle
B. User pays
principle
C. Cradle to the
grave principles
D. all of above
Answer: (D)
49. The objective of Environmental Management
Plan (EMP) is to formulate measures which will:
A.
Mitigate adverse impacts on various environmental components, which have been
identified during the rapid environmental impact assessment study.
B.
Protect environmental resources where possible.
C.
Enhance the value of environmental components where possible.
D.
All of the above
Answer:
(D)
50.
The environmental management plan covers the
A.
Design
B.
Construction
C.
Management
D.
All of the above
Answer:
(D)
51.
What is the term given to the idea that different people may have different
viewpoints on environmental management?
A.
Environmental ethics
B.
Environmental economics
C.
Tragedy of the commons
D.
Sustainable development
Answer:
(A)
52.
Which of the following statements is correct?
A.
Human induced environmental change is usually more rapid than natural change
and broadly irreversible
B.
There is only one type of environmental management option, to stop the cause of
change
C.
For a successful management option to be decided it is best to limit the number
of stakeholders to those with the greatest interest only
D.
Environmental management is based on the premise that an environmental problem
has to be managed only if it has been proven to cause a major problem
Answer:
(A)
53. .................. deals with the management
of the environment without any kind of human interference with nature.
A.
Protection
B.
Prevention
C.
Conservation
D.
Rehabilitation
Answer:
(B)
54.
....................... approach emphasis on human adjustment with physic
biotic environment in relation to techno-behaviour institutional adjustments
A.
Protection
B.
Prevention
C.
Conservation
D.
Rehabilitation
Answer:
(C)
55.
................dictates that anyone who disturbs or spoils the environment in
any way must take necessary corrective measures to rectify the environment or
pay for the cost of remediation
A.
Polluter Pay Principle (PPP)
B.
Precautionary Principle (PP)
C.
Intergenerational Equity Principle (IEP)
D.
Cradle to the grave principles
Answer:
(A)
56.
...................... implies promoting systems that, where possible, enable
people to enact their own forms of pro-social and pro-environmental behaviour
through voluntary, not coerced, cooperation.
A.
Polluter Pay Principle (PPP)
B.
User pays principle (UPP) (or resource pricing principle)
C.
Precautionary Principle (PP)
D.
Subsidiary Principle (SP)
Answer: (D)
57. Which of the
following UN commission is responsible for reviewing progress in the
implementation of Agenda 21 and the Rio Declaration on Environment and
Development?
A. United Nation
Disaster management Commission
B. United Nations
Statistical Commission
C. United Nations
Commission on Sustainable Development
D. United Nations
Commission on Human Rights
Answer:
(C)
58. Innovation is defined as:
a. The commercialization of a new
product or process.
b. the invention of a new product
or process.
c. a new product or process idea.
d. the implementation of a new production method.
Answer: (A)
59. ______________ shows the
process of creating something new.
A. Innovation
B. Business model
C. Modelling
D. Creative flexibility
Answer: (A)
60. Innovations provide
A. The primary means for
differentiating your product from your competitors'
B. Higher profit margins
C. Potential barriers to entry
D. All of the above
Answer: (D)
61. Who is not needed in
developing participation for innovation in the organizations?
(i) Role Model
(ii) Catalyst
(iii) Investor
(iv) Customer
A. Only (iv)
B. Only (iii) and (ii)
C. Only (iii) and (iv)
D. Only (i)
Answer:
(C)
62. Which of the following is/are
challenge(s) in the process of innovation?
A. Fear of failure
B. Unable to predict
C. Lack of resources
D. All of the above
Answer:
(D)
63. Which of the following is
correct?
A. Innovation starts with
creativity.
B. Innovation begins with
curiosity.
C. Innovation happens accidentally.
D. All of the above
Answer:
(B)
64. Which of the following is/are
not an objective (s) of sustainable development?
A. Continue to implement the family
planning program
B. Maintain a dynamic balance of
arable land (not less than 123 million hectares) and implement an agricultural
development strategy
C. Maintain a dynamic balance of
water resources by reducing water consumption for every unit of gross development
product growth and agricultural value added
D. To bring about a gradual and
sometime catastrophic transformation of environment
Answer:
(D)
65. What are the Primary Goals of
Sustainability?
I. The end of poverty and
hunger
II. Better standards of education
and healthcare - particularly as it pertains to water quality and better
sanitation
III. To achieve gender
equality
IV. Sustainable economic growth while
promoting jobs and stronger economies
A. I, II & III
B. I, III & IV
C. I & III
D. I, II, III & IV
Answer: (D)
66. Consider the following
statement (s) related to the parameters of sustainable development refer to the
guiding principles.
I. Help in understanding the concept
of sustainable development
II. Point the problems associated
with it
III. Help to take active policy
measures
A. Both I & II
B. Both II & III
C. Both I & III
D. I, II & III
Answer:
(D)
67. Which of the following is not
included in the parameters of sustainable development?
A. Carrying capacity
B. Inter and Intra-generation
equity
C. Gender disparity and diversity
D. None of the above
Answer:
(D)
68. How many Sustainable
Development Goals (SDGs) have been agreed to, by all the world’s nations, as
part of the 2030 Agenda?
A. 17 B. 10 C.8 D.16
Answer:
(A)
69. Goal 1 is about poverty. What
is the aim of this Goal?
A. Cut poverty in half by 2030
B. Reduce poverty by 75% by 2030
C. End poverty in all its forms
everywhere
D. Help each nation make progress
on reducing poverty
Answer:
(C)
70. Goal 17 is about
strengthening the “means of implementation” and revitalizing the “Global
Partnership” for realizing all the other Goals. Which of the following is not
part of Goal 17?
A. Mobilizing the financial
resources necessary to achieve the Goals
B. Creating international sports
tournaments and festivals to promote the Goals
C. Helping developing countries
build the capacities they need in areas such as technology, public policy, and
data for reporting on progress
D. Enhancing trade, especially to
help developing countries increase their exports and grow their economies
Answer:
(B)
71. Which of the following is not
part of the Sustainable Development Goals?
A. Access to sustainable energy
for all
B. Availability of water and
sanitation for all
C. Provision of internet services
for all
D. Promotion of decent jobs for
all
Answer:
(C)
72. Equality issues are
specifically mentioned in how many of the Sustainable Development Goals (not
including the targets)?
A. In two of them: Goal 6 on
water, and Goal 12 on sustainable production and consumption
B. In four of them: Goal 2 on
hunger, Goal 7 on energy, Goal 8 on economic growth and jobs, and Goal 14 on
preserving the oceans and seas
C. In three of them: Goal 4 on
education, Goal 5 on gender, and Goal 10 on reducing inequality within and
among countries
D. In one of them: Goal 16 on
promoting peaceful and just societies for all
Answer:
(C)
73. Which of the following is not
part of Goal 15, on ecosystems?
A. Halt and reverse land
degradation
B. Halt biodiversity loss
C. Halt the use of biotechnology
and genetic engineering
D. Use ecosystems sustainably
while protecting and restoring them
Answer: (C)
74. Which of the following is not
true about the SDGs?
A. They encourage the promotion
of health, well-being, and education for all, at all ages
B. They explicitly promote
innovation
C. They include the development
of sustainable cities, infrastructure, and industry
D. They are a legally binding
international treaty that all nations are required to follow
Answer:
(D)
75. What can individuals do to
help realize the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals?
A. Hold their governments and the
private sector accountable and support reputable civil society organizations
B. Create projects and
partnerships of their own and participate in existing initiatives to help
achieve one or more of the goals
C. Use their positions in society
— as teachers, decision-makers, consumers, role-models, and ordinary citizens —
to voice support for the Goals, to make decisions that advance the Goals, and
to take actions help to implement the Goals
D. All of the above
Answer:
(D)
References
https://www.examveda.com/
https://www.sanfoundry.com/
https://www.indiabix.com/