Disclaimer:
This document does not claim any originality and
cannot be used as a substitute for prescribed textbooks. I would like to
acknowledge various sources like freely available materials from internet
particularly NPTEL/ SWAYAM course material from which the lecture note was
prepared. The ownership of the information lies with the respective authors or
institutions. Further, this document is not intended to be used for commercial
purpose and the BlogSpot owner is not accountable for any issues, legal or
otherwise, arising out of use of this document.
This open resource is a collection of academic course under the graduation program for B. Tech (Civil) prepared as per the syllabus of the Dr. B.A.T University, Lonere, Raigad (m.s), India by Dr. Mohd. Zameeruddin, Associate Professor, of MGM's College of Engineering, Nanded for use in out-of-class activity. The content covers both theoretical and analytical studies. There are six lessons as part of this document, and each deals with an aspect related to the Basics of Civil Engineering.
Unit 1: Introduction and role of Civil
Engineer
Unit 2: Study of Engineering Materials
Unit 3: Component parts of Structures
Unit 4: Surveying and Levelling
Unit 5: Building Planning
Unit 6: Environmental Engineering
Unit
1: Introduction to Civil Engineering
Civil engineering is the oldest branch of engineering which is growing
right from Stone Age civilization. American Society of Civil Engineering (ASCE)
defines civil engineering as "the profession in which knowledge of mathematical and physical sciences
gained by study, experience, and practice is applied with judgment to develop
ways to utilize economically the materials and forces of nature for the
progressive well-being of man".
To understand the definition let us have an analogy:
Once, a strong debate held between the various organs of a human body
on the topic of superiority. At the start of the debate brain said I am the
superior, I send instructions and control messages, you follow it, I memorize
the past and present and you follow them.
Heart interrupts saying, no brother, I am
superior because if I stop pumping blood you people will not survive. The lungs
also added their voice saying we are superior if we stop to breathe, your life
will get stopped. Kidneys also get involved in the debate stating the function
of purification of blood.
Meanwhile, skin who was hearing all these
statements, feel sorrow about itself that I don't perform any specific task. So
I don't have right to stay in the body. Hence get self downed from the body.
Suddenly the debate among the organs stopped, as they saw that a Tiger is
approaching towards them.
The body starts running from the place. While running the body starts maintaining all organs in their positions by hands, which were getting thrown out. All organs unitedly shout, the skin where are you, you are the superior one, not us. You shaped us, please save us.
In similar way all branches of engineering are good, but one who covers all sectors of society is civil engineering. According to me civil engineering is a civilization. It starts when you wake up and ends when you sleep. A schematic application of civil engineering is shown in Figure 1.
Role of a Civil Engineer
A civil engineer has to conceive, plan,
estimate, get approval, create and maintain all civil engineering
infrastructure activities. A civil engineer has a very important role in the
development of following infrastructures.
1.
To measure and map the earth’s surface.
2.
To plan and develop extensions of towns and
cities.
3.
To build the suitable structures for rural
and urban areas for various utilities.
4.
To build the tanks and dams to exploit water
resources.
5.
To build river navigation and flood control
project.
6.
To build canals and distributaries to take
water to agricultural fields.
7.
To provide purification and distribution
units for freshwater.
8.
To provide and maintain communication system
like roads, railways, harbours and airports.
9.
To provide, build and maintain drainage and
waste water disposal system.
10. To monitor land, water, and air pollution and take measures to control them. Fast growing industrialization has put heavy responsibilities on civil engineers to preserve and protect the environment.
Role of civil engineer in the field of;
Surveying and Levelling
Surveying is
a science and art of determining the relative position of different objects on
the surface of the earth, by measuring linear and angular distance, directly or
indirectly to prepare a map. In the surveying, the measurement of distance
relates to the horizontal plane. Surveying is broadly classified as;
|
1. Land Survey |
2. Topography Survey |
|
3. Cadastral Survey |
4. Engineering Survey |
|
5. City Surveys |
6. Marine or Hydro graphic Survey |
|
7. Astronomical Survey |
8. Photographic Survey |
|
9. GPS Survey |
|
Levelling is the art of
determining the relative vertical distances of different objects on the surface
of the earth. The levelling relates with the vertical plane in reference to a
datum (That is, Mean Sea level, MSL). Levelling is broadly classified as;
|
1. Simple Levelling |
2. Differential Levelling |
|
3. Fly Levelling |
4. Check Levelling |
|
5. Profile Levelling |
6. Cross Levelling |
|
7. Reciprocal Levelling |
8. Trigonometric Levelling |
|
9. Barometric Levelling |
10. Hypsometric Levelling |
Figure 2, illustrates application and instruments used in surveying and levelling. With the knowledge of surveying and levelling
a civil engineer helps for preparing maps and plans for various applications in
engineering projects as listed below;
1.
Land
survey for the purpose of taxation and implementation of revenue policies.
2.
Topography
survey describing the natural features of area
3. Route
survey for fixing of alignment of proposed route, the location of bridges,
culverts, etc.
4.
City
and municipal survey for defining cadastral property, zoning, green belts, etc.
5. Construction
survey for the location of material quarries, site drains, marking and layouts,
etc.
6.
Hydro-graphical
survey for knowing the hydrological details such high flood marks, etc.
7.
The
photographic survey used to have an aerial survey of flood-affected areas,
dense forest, etc.
8. Marine Survey to Identify the marine fossils, rock beds, ocean surface, etc.
9. Mine survey to identify or locate mineral ores, depth, and age of fossils, etc.
10.
Forensic
survey and geological survey to find facts related to causes of failures, etc.
With the knowledge of Levelling civil
engineer helps in preparing maps and plans for various applications in
engineering projects as listed below;
1. To
prepare a contour map for fixing sites for reservoirs, dams, barrages, fix the
alignment of roads, railway, irrigation canals, etc.
2. To determine the altitudes of different important points so as to determine the reduced levels with reference to datum
3. To prepare layout plans for water supply, sanitary or drainage
Construction Management
The construction process is a complex activity which involves planning, designing, execution, transportation and storage of materials, equipment, labour. To have effective and economical construction a civil engineer must possess strong and experienced management skill.
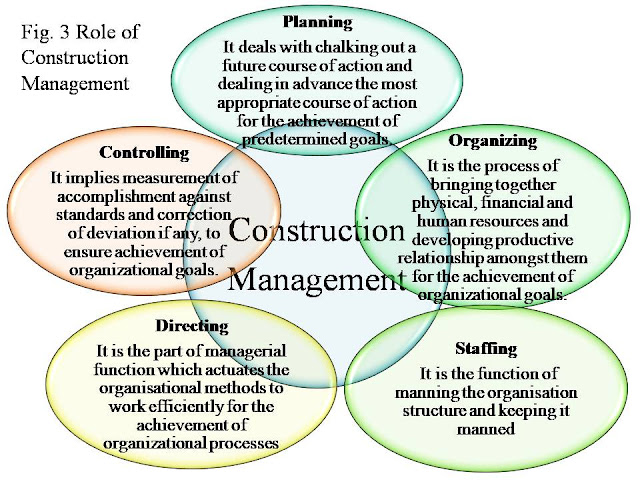
Construction management is the process of planning, coordinating, monitoring and scheduling of a construction activity which is termed as Project planning and Management. Construction management concepts add following advantages to a project;
Optimum utilization of resources.
Reduction in the cost of construction by using best combination of material/ workmanship/ equipment's available.
Achieving balance between the changing environment/ changing demands of market/ changing needs of society.
Building essentials for prosperity of society.
Figure 3, illustrates
the role of construction management in a construction project.
Structural
Engineering:
Structural
engineering is the science and art of designing and making, with economy and
elegance, buildings, bridges, dams and other similar structures by utilizing
the different combination of materials and geometry so that, they can safely
resist the forces to which they may be subjected.
Structures are subjected to various type loads like dead loads, live loads, snow loads, impact loads, wind loads, seismic loads and their combinations. These loads are transferred safely to the ground by predefined load path made by arranging various structural components.
During this transfer structural components are subjected to internal stresses like tension, compression, bending, and torsion. A designer has to ensure that structural member shall be able to sustain applied loads without exceeding limits of stresses and strains. The process of calculating the loads, their combinations, and effects on a structural component or geometry is called as structural analysis. The procedure of estimating the required cross-sectional area of material to sustain applied load within the acceptable limits of safety and serviceability is termed as structural design.
A Civil Engineer during his academic life learns about the forces and
their effects, materials and their strength, structural assemblages, geometric
configurations and is capable to utilize these skills in the optimization of
structural analysis and structural design. The various examples of complex
structures design by civil engineers can be identified from the Pyramids of
Egypt, Eiffel Tower, to the modern era Burj Khalifa and Bandra-Worli Sea Link.
Structural Engineer performs following roles;
Identification and classification of various types of structures.
Estimation of various loads attracted by the structure.
Predicting the limits of safety and serviceability for both material and structural component.
Analysis of different structures and predicting its behaviour.
Design of different structural components and optimization of their geometry
Economical and ease structures
Figure 4, illustrates various structural designs done by a Structural
Engineer.
Transportation Engineering:
Transportation Engineering involves the
application of scientific and technological principles to any mode of transport,
to provide safe, economic and rapid movements of goods and people from one
place to another place.
Highway Engineering
Railway Engineering
Airport Engineering
Waterway Engineering
Bridge and Tunnel Engineering
City and Urban roads
Traffic Engineering
Dock and Harbor Engineering
Engineers in this specialization:
Handle the planning, design, construction, and operation of highways, roads, railways, airports, harbors and other vehicular facilities as well as their related bicycle and pedestrian realms.
Estimate the transportation needs of the public and then secure the funding for projects.
Analyze locations of high traffic volumes and high collisions for safety and capacity.
Use engineering principles to improve the transportation system. Utilize the three design controls, which are the drivers, the vehicles, and the mode of transport.
Among the three basic needs food,
water and shelter, water is a vital need. Water available on earth is a gift
given by almighty. 71 percent of the world surface is covered with water. Among
this available source only 3 percent water is usable.
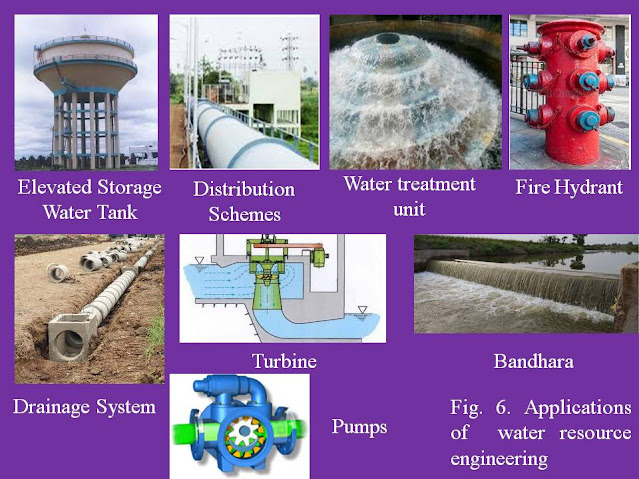
In addition to the use for drinking, water is needed for agriculture, industry, and daily needs. Rains appear in seasonal basis, so water is not available throughout the year. That's why it is needed to store the water, so as to supply it whenever demanded. A civil engineer plays an important role in storage of rain water and its supply. The applied field of civil engineering in water supply and management is (Ref. Figure 6);
1. Water supply Engineering
2. Sanitary Engineering
3. Water resource Engineering
4. Hydraulics
5. Waste water treatment
In water supply engineering,
civil engineer is engaged with design, construction and maintenance of a water
supply scheme. He evaluates the demand of water, assures quality of water,
design of water storage tanks, layout of the distribution system, design of
pipes and pumps, design of water treatment plant, and fire hazard outlets.
The water after the use comes out
of the house-hold as a sewage which has to be disposed safely back to the
rivers or canals. Before the disposal of this contaminated water it’s require
to treat. This treatment process is called as sanitary engineering. In sanitary
engineering, civil engineer performs the role of designing of sanitary units,
drainage lines, sewer appurtenances, wastewater treatment units.
Water is not available throughout the year, so proper storage reservoirs are needed. Civil engineers play a role of estimating the quantity of water required to be stored. He identifies the location and catchment areas for required capacity. He designs, artificial brackets like dams, spillways, bandhara across the rivers. He designs the canals for irrigating the fields. He designs the additional sources of outputs from irrigation engineering like hydro-power engineering and lift irrigation units.
Hydraulic engineering involves the study of mechanics of forces acting on the bodies due to fluids. It involves study of fluid statics and fluid dynamics. A civil engineer does the dimensional analysis, design of pumps, design of turbines, design of hydraulic gates, and analyse the nature of the flow.
A civil engineer also performs the task of treating the waste water coming from various industrial units, before it being dispose back to streams, channels or rivers.
Geo-technical Engineering:
Geo-technical engineering is a
civil engineering discipline that deals with the study of soil and rock behavior in an engineering perspective. The study of the formation of soil and rocks is
needed for a civil engineer for the use in the design and construction
different structures.
The term "soil" can have different meanings,
depending upon the field in which it is has been referred.
To a geologist, it is the
material in the relative thin zone of the Earth's surface within which roots
occur, and which are formed as the products of past surface processes. The rest
of the crust is grouped under the term "rock".
To an agriculturist, it is the
substance existing on the surface, which supports plant life.
To a civil engineer it is a
composite of the granular matrix which provides resistance to the heavy loads
coming from the structure.
The earth is made of three major
parts inner core, outer core and the crust. The crust appears in the form of
terrestrial and oceanic crust. The structures are constructed on the surface of
terrestrial and ocean crust. The top layer of crust composition of the loose
soil, which is fertile one, possesses less strength against heavy loads.
As we go
deep into the soil the strength of the soil improves, also the structure
changes from soft rock to hard rock.
The formation of the rock is
classified as sedimentary, metamorphic and igneous. In the Earth's surface,
rocks extend up to as much as 20 km depth. The disintegration of rock by the
weathering, decomposition and erosion result into the soil mass. The study of
the soil formation and rock mechanics is termed as soil mechanics or
Geotechnical engineering. With the knowledge of soil mechanics, civil engineer
performs the following skill jobs (Refer Fig. 7):
- Design and construction of suitable foundation for buildings, bridges, and other infrastructural works
- Design and construction of earthen dams and embankments
- Design and construction of minor irrigation works like barriers, bunds and canals for irrigation
- Design of embankments for highways, railways, helipads and runways
- Design and construction of earth retaining structures
- Design layout plan for tunneling operation in hills and valleys
The major soil parameters focused
under the soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering is permeability,
stiffness, and strength.
Unit 2: Study of Engineering Materials
In
modern construction of the buildings and other infrastructural developments
backed by engineering technology, building materials plays an important role.
This
building material study includes;
- Soil, Rocks, Stones and Aggregates
- Bricks
- Cement
- Lime
- Concrete and Mortar
- Timber
- Steel
What is a Concrete?
Concrete is the mechanized mixture of, cement, fine aggregates, coarse aggregates and water in certain proportions which results in a matrix that hardens (cures) over time and gains a design strength.
Concrete is designated in reference to its characteristic strength. For example M 5; where M specifics the mix proportion and 5 shows the compressive strength of cube at an age of 28 days from the day of making a mix.
Concrete mixes are classified as; (a) ordinary concrete, (b) standard concrete and (c) high strength concrete. The classification is based on accuracy of preparation of mixes. Table 1 provides detail classification of all such concrete mixes used in practice.
Table 1: Grades of concrete
|
Group |
Grade designation |
Specified characteristic strength of
150 mm cubes at 28 days in MPA |
|
Ordinary Concrete |
M10 |
10 |
|
M15 |
15 |
|
|
M20 |
20 |
|
|
Standard Concrete |
M25 |
25 |
|
M30 |
30 |
|
|
M35 |
35 |
|
|
M40 |
40 |
|
|
M45 |
45 |
|
|
M50 |
50 |
|
|
M55 |
55 |
|
|
High Strength Concrete |
M60 |
60 |
|
M65 |
65 |
|
|
M70 |
70 |
|
|
M75 |
75 |
|
|
M80 |
80 |
What
is a characteristic strength of a concrete?
The compressive strength of
concrete is given in terms of the characteristic compressive strength of 150 mm
size cubes tested at 28 days (fck). As per IS 456-2000, the characteristic strength is defined as
that strength of the concrete below which not more than 5% of the tests results
are expected to fall. That is there is 5% probability or chance of actual
strength being less than the characteristic strength.
There may exits considerable differ between the actual value of cube strength at the site compared to theoretical value or design value of cube strength. This difference may be attributed towards the preparation of concrete mix in the control condition in the laboratory compared to the uncontrolled state of mix preparation on site.
These variations in strength are obtained from the frequency distribution curve by plotting the frequency ordinates at different intervals. If the obtained variation is normal, the curve is called normal (Gaussian) distribution curve. The value corresponding to peak of the curve is called as the mean value. The normal distribution curve is symmetrical along both the sides (see figure 9). The shaded region shows the probability of the fall in the characteristic strength.
The characteristic strength (fck) is obtained as;
fck = fm – kS
Where;
fck is Characteristic
strength
fm is mean
strength
S is standard deviation = √ (observed
deviation) / (No. of samples -1)
k is probability constant (for 5%
equals to 1.64)
Stone
What is a Concrete?
Concrete is the mechanized mixture of, cement, fine aggregates, coarse aggregates and water in certain proportions which results in a matrix that hardens (cures) over time and gains a design strength.
The size of the gutter should be according to the flow during the highest intensity rain. It is advisable to make them 10 to 15 per cent oversize. Gutters need to be supported so they do not sag or fall off when loaded with water. The way in which gutters are fixed depends on the construction of the house; it is possible to fix iron or timber brackets into the walls, but for houses having wider eaves, some method of attachment to the rafters is necessary.
- Vertical loads,
- Horizontal loads, and
- Longitudinal loads.

- Dead loads
- Live loads
- Dynamic loads
- Wind loads
- Earthquake loads
- Snow loads






































































Very nice post! You provide a concept is very useful for increasing myself. I am regularly read your blog and keep sharing with us.
ReplyDeleteOracle DBA Training in Chennai
Oracle DBA Course in Chennai
Spark Training in Chennai
Excel Training in Chennai
Corporate Training in Chennai
Tableau Training in Chennai
Oracle Training in Chennai
Oracle Apps DBA Training in Chennai
Oracle DBA Course in Velachery
It's a magnificent blog!thanks for sharing this wonderful information.
ReplyDeleteGerman Classes in Chennai
German Language Classes in Chennai
TOEFL Classes in Chennai
german language course
French Language Classes in Chennai
best german classes in chennai
german classes
German Classes in vadapalani
German Classes in thiruvanmiyur
German Classes in t nagar
This is a fabulous post I seen because of offer it. It is really what I expected to see trust in future you will continue in sharing such a mind boggling post environmental test chamber
ReplyDeleteNice post! This is a very nice blog that I will definitively come back to more times this year! Thanks for informative post. civil engineering books
ReplyDeleteNice to read your article! I am looking forward to sharing your adventures and experiences. presentation skills training singapore
ReplyDeleteThis blog has been helpful mostly for Civil Engineer students
ReplyDeletethanks for sharing informative ideas and blogs
online training for civil engineer
Your website is very informative and Articles are very good.
ReplyDeleteQuantity surveying Course
ReplyDeleteAmazing sir. very interesting facts about civil engineers and informative blog post.
Portable Site Offices for contact us. Structural Steel Fabrication, Structural Steel Erection Services,
Your website is very informative and Articles are very good.
ReplyDeleteBilling Engineering Course